Article de Xingci CHEN (MS EnvIM 2023-24)
Introduction
For the past seven years, my mornings have been marked by a peculiar ritual : the 7:24 alarm on my phone. It’s not a typical wake-up call; rather, it’s a signal for me to collect “green energy” for my Ant Forest. 7:24 is the moment when the energy accumulated from my eco-friendly actions the previous day gets mature, and ready to be harvested.
If I miss this window, my hard-earned “green energy” risks being poached by my friends. In Ant Forest, every time I engage in green behaviors like taking public transportation, choosing paperless receipts, and walking, I earn “green energy” the next morning. By collecting this energy, I can exchange it for real trees, which Ant Forest plants in desertification-prone areas, especially in northwest China.
Now, you might wonder, is it truly worth sacrificing precious sleep for the sake of virtual rewards? It’s a valid question, one that I’ve pondered many times myself. But to me, Ant Forest is more than just a game—it’s a conduit through which I, an ordinary individual, can contribute to environmental preservation on both local and global scales. Its significance transcends mere entertainment; it’s a catalyst for personal growth and societal change.
In this blog article, we’ll delve into the multifaceted significance of Ant Forest, exploring its economic, social, and environmental implications. From its role in incentivizing sustainable behavior to its potential to catalyze broader shifts in societal norms, we’ll unpack the far-reaching impact of this seemingly simple app. So join me as we unravel the layers of Ant Forest and uncover the profound transformations it has instigated—transformations that extend far beyond the confines of my early morning wake-up call.
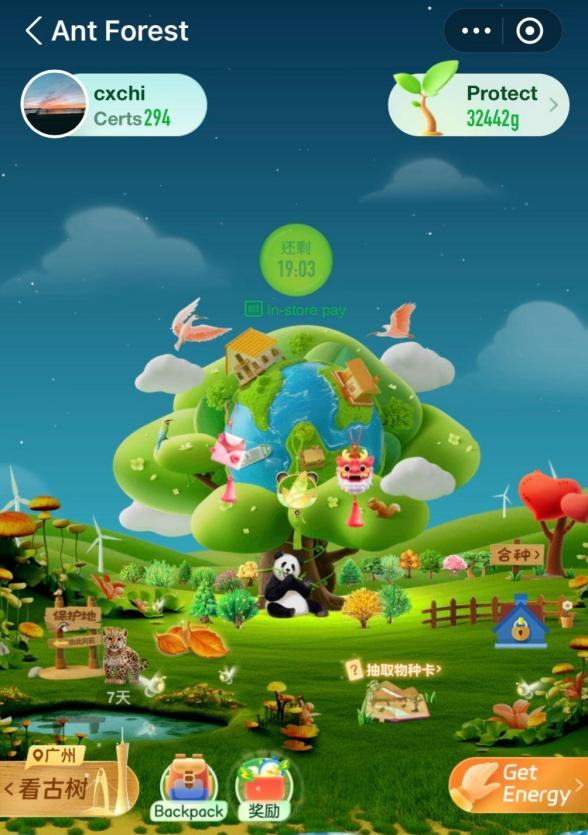
What Is Ant Forest ?
The Ant Forest is a pioneering CSR initiative under Alipay, a subsidiary of Ant Financial Services, which in turn is part of the renowned Alibaba Group. Launched in 2016, this innovative platform has provided users with an avenue to establish and manage personal carbon accounts, primarily through tree planting initiatives alongside a plethora of other social projects (SMU City Perspectives team, Growing A Global Forest).
By seamlessly integrating social interaction and gamified elements, Ant Forest not only fosters entertainment but also serves as a catalyst for promoting environmental stewardship. With a strong emphasis on encouraging eco-conscious actions, the platform has garnered substantial support from the Chinese government. It aligns with China’s unwavering commitment to environmental conservation and sustainable development, symbolizing a national resolve to address pressing ecological concerns.
Through the establishment of “carbon accounts,” Ant Forest empowers Chinese citizens to actively engage in environmental protection initiatives and make tangible contributions to reducing their carbon footprint. This collective effort underscores China’s proactive stance on environmental issues, signaling a concerted push towards a more sustainable future for both the nation and the planet as a whole.
Achievement & Impact
As of 2023, in the span of seven remarkable years since its inception, among the over one billion users of Alipay, over half a billion use Ant Forest to engage in eco-friendly activities (Zhao, M., & Abeysekera, I, 2024). It has emerged as a formidable force for environmental conservation and community empowerment.
Through strategic partnerships with over 20 public welfare organizations, the platform has facilitated the planting of an astounding 475 million trees (Tao, 2023). This monumental effort has not only contributed to the establishment of 31 nature reserves but has also played a pivotal role in supporting ecological initiatives across 22 provinces, including regions as diverse as Inner Mongolia and Gansu (Tao, 2023).
The impact of Ant Forest extends far beyond tree planting initiatives. By fostering collaboration with local communities, the platform has created meaningful employment opportunities for over 3.7 million individuals involved in various aspects of ecological conservation, from planting and maintenance to patrolling (Tao, 2023). This symbiotic relationship between environmental stewardship and economic empowerment underscores Ant Forest’s commitment to holistic sustainability. What sets Ant Forest apart is its innovative approach to public welfare practices.
Through a trifecta of advancements in project management, consolidation of ecological achievements, and meticulous supervision of public welfare funds, the platform has redefined the landscape of environmental activism. By leveraging technology and fostering transparency, Ant Forest has not only streamlined operations but has also enhanced accountability, ensuring that every contribution yields tangible results.
Moreover, Ant Forest’s initiatives have served as a catalyst for socio-economic development in rural areas. In addition to creating jobs for farmers by planting trees in the desert, Ant Forest provides income-generating opportunities for local people. For example, in November 2018, Ant Forest introduced its first ecological economic tree species, the “Seabuckthorn.” By December 9, 2019, Ant Forest began selling seabuckthorn juice online.
After covering the costs of raw material harvesting and processing, all proceeds are donated to the China Foundation for Poverty Alleviation to support ecological protection, poverty alleviation, and income growth in central and western regions. Through Ant Forest, Alipay is dedicated to transforming the “ecological benefits” of seabuckthorn forests into “economic benefits” for poor areas (Pi, 2019).
This initiative bridges the gap between environmental protection and poverty alleviation, safeguarding natural resources while promoting sustainable livelihoods, creating a win-win situation for both humanity and the planet.
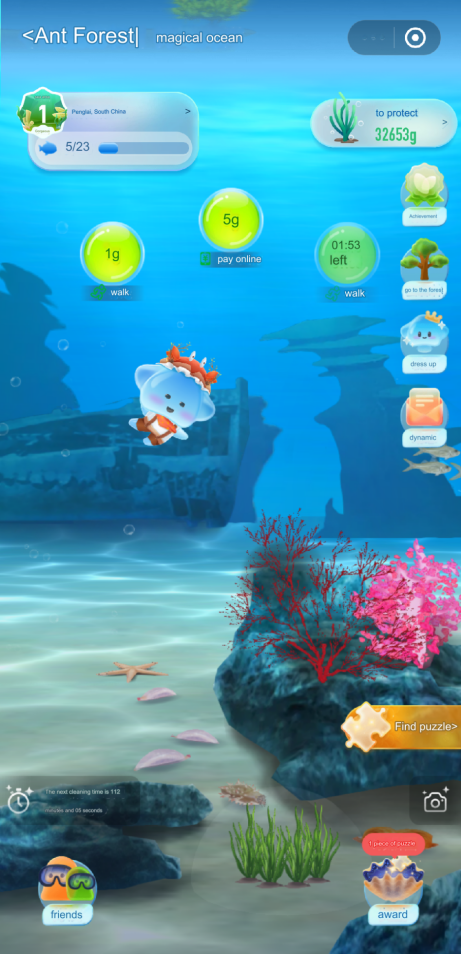
Ant Forest’s commitment to innovation knows no bounds, extending beyond traditional business models to embrace novel approaches in environmental conservation. A testament to this forward-thinking ethos is the launch of the Magic Ocean section in 2021, marking a significant expansion of the platform’s scope from terrestrial to marine ecosystems (Ant Forest – Magic Ocean, 2022). Magic Ocean offers users a captivating 3D immersive experience that fosters awareness and engagement in marine ecological protection (Ant Forest – Magic Ocean, 2022).
The interactive features of Magic Ocean empower users to play an active role in conservation efforts by cultivating and planting marine plants, as well as cleaning up sea area garbage virtually. This hands-on approach not only instills a sense of ownership and responsibility but also fosters a deeper connection to marine ecosystems.
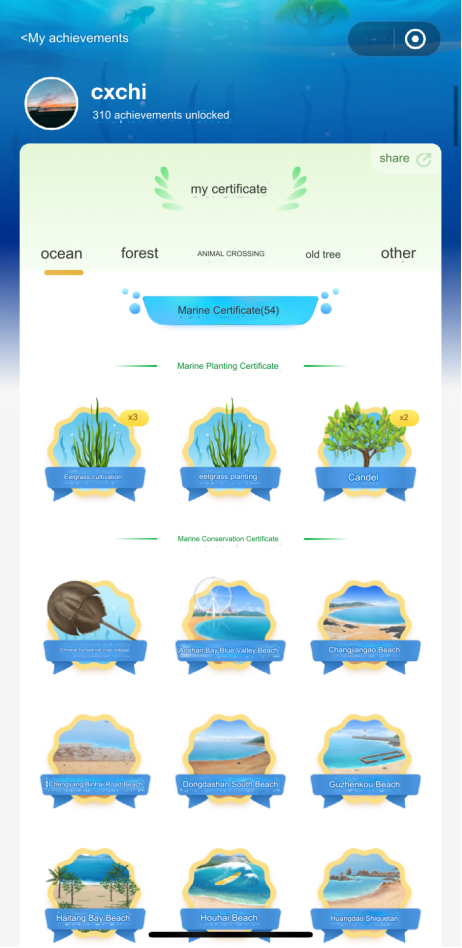
The same as Ant Forest, Magic Ocean integrates authentic planting certificates and educational content related to the environment, specific to marine ecology. As users progress through each level, they not only contribute to real-world conservation efforts but also gain valuable insights into the importance of preserving our oceans and the diverse life forms they support.
Social Engagement
The enduring appeal of Ant Forest lies in its unwavering dedication to enhancing user engagement and promoting public welfare (Yang, Kong, Sun & Zhang, 2018). By instilling a sense of accomplishment and personal connection, the platform not only attracts new users but also fosters loyalty among its existing community. Allow me to delve into a few ingenious design concepts within Ant Forest that exemplify this principle.
First and foremost, Ant Forest’s Reward Mechanism stands as a paragon of user-centric design. Through this well-crafted system, users earn green energy by completing eco-friendly actions, which they can then utilize to plant trees. Each planted tree is assigned a unique number and is genuinely planted in designated areas across China, a tangible testament to users’ environmental impact.
The platform goes a step further by providing users with daily progress reports and live area cameras, allowing them to witness the growth of their trees firsthand (Rapp, 2018). Additionally, Ant Forest recognizes and rewards user dedication with annual tree planting badges and physical tree planting certificates, along with charming peripherals like postcards and stickers. This thoughtful approach not only bolsters user retention but also enhances the platform’s playability, ensuring a deeply engaging experience for all.
Secondly, on May 22, 2020, recognized as “International Biodiversity Day,” Ant Forest, in collaboration with the China Environmental Protection Foundation and the Shanshui Nature Conservation Center, launched the “Protect Together: Everyone Owns One Square Meter” biodiversity initiative under the guidance of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (BiaNews, 2020). Through this initiative, except for planting trees, individuals can use green energy to “claim” a one-square-meter protected area within the Sanjiangyuan region of Qinghai. Protected areas like these are being announced and open to be “claimed”regularly, alongside with the development of Ant Forest.
Thirdly, on May 22, 2023, another International Biodiversity Day, Ant Group forged partnerships with relevant authorities in Guangzhou, Hangzhou, and Nanjing to launch the “Public Welfare Support Project for Ancient Tree Protection.” Through this initiative, iconic ancient trees in each city were introduced to the Ant Forest platform.
Ant Group’s commitment to donate funds to support local governments in the preservation and maintenance of these ancient treasures underscores its dedication to environmental stewardship. By connecting users with trees that have stood witness to the history of their communities, this project fosters a deep sense of emotional connection and civic pride. By tapping into users’ love for their hometowns, initiatives that resonate with their communities evoke a powerful emotional response, further strengthening their engagement with Ant Forest.
In essence, Ant Forest’s success lies not only in its innovative features but also in its ability to forge meaningful connections with users. By fostering a sense of accomplishment, personal connection, and civic responsibility, the platform transcends mere entertainment, becoming a powerful tool for environmental conservation and community empowerment.
Continuance Mechanism & Sustainable loop
Ant Forest uses its gamification continuance mechanism to enhance user stickiness, crafting a sustainable loop that draws participation from the Ant Forest project team, Alibaba Group, ordinary citizens, and governmental entities, thus forming a beneficial cycle of sustainable development.
The game design and rule mechanism links people’s ant forest accounts with their real behaviors. Throughout the day, users conscientiously monitor their own behaviors, striving to maximize energy harvest through eco-friendly actions. Personally, I’ve reevaluated my travel habits; while my default choice used to be driving, the allure of 52g of energy from a single public transit ride prompts me to reconsider, opting for greener alternatives.
Internally, this mechanism not only incentivizes customers to adopt eco-conscious lifestyles but also benefits the company. Customers seeking energy must utilize Alipay payment codes for subway rides, thereby recording their transactions. Consequently, Ant Forest encourages greener living while positioning Alipay as the preferred payment platform for environmentally conscious individuals.
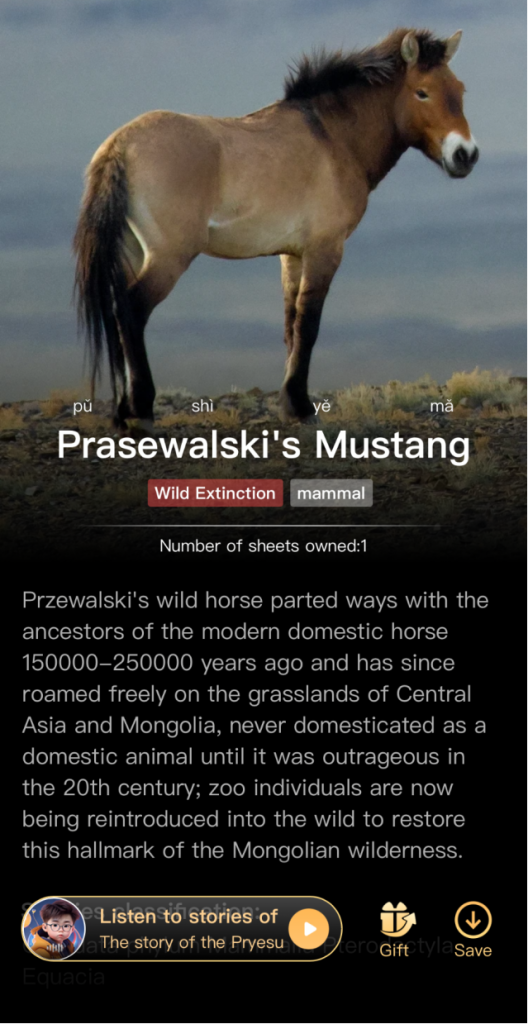
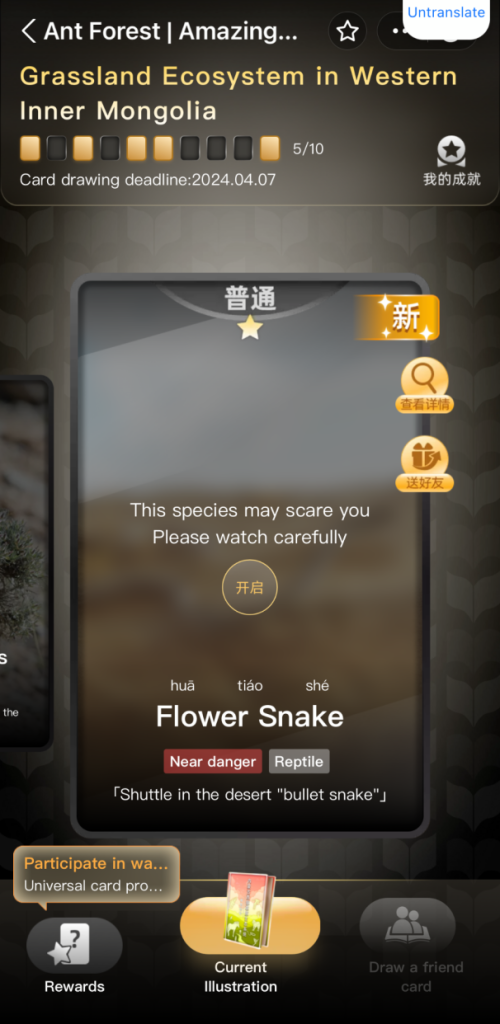
Furthermore, Ant Forest leverages technology and innovation to bolster user retention and attraction. Regular updates introduce new features and environmental initiatives, such as the upcoming “Magic Animals” project slated for 2021. Through this initiative, users collect endangered animal identity cards via daily draws, supplemented by educational videos and textual insights. Beyond environmental endeavors, Ant Forest integrates various social and economic impact initiatives, including “Ant Farm” and “Ant Village.”
While Ant Farm focuses on aiding people in rural areas economically, users in Ant Farm raise a virtual chicken, gaining feed through green behaviors and eventually using the eggs their chicken lays to donate to organizations that help people, for example supporting children with congenital heart disease. The platform also enables direct monetary and material contributions, democratizing philanthropy and emphasizing that impactful contributions need not be monetary.
This gamified approach keeps users engaged, fostering healthy competition within social networks. In a report responding to Ant Forest, Erik Solheim, head of United Nation Environment Programme, mentioned that “two hundred million people—that’s 3% of the world’s population—are greening their lives because they are getting immediate information about the environmental impact of their choices in a fun and competitive way. This shows that digital finance holds a huge untapped power to mobilize people in support of sustainable development and the fight against climate change. And this power is literally at our fingertips through our mobile devices (UNEP, 2017).”
Ant Forest’s Future Path
The fusion of internet technology with green public welfare initiatives has emerged as a powerful force in promoting sustainable lifestyles worldwide. Ant Forest, a flagship example of this phenomenon, has captivated millions of Chinese millennials, compelling them to embrace sustainable practices in their daily lives. By gamifying environmental conservation and incentivizing green behaviors, Ant Forest has successfully harnessed the power of technology to promote eco-consciousness on a massive scale.
The key to its success lies in its ability to resonate with users across diverse demographic groups, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries. While Ant Forest has flourished in China, its principles and mechanisms hold promise for application in other countries seeking to promote sustainable development. By leveraging the ubiquity of smartphones and digital platforms, similar initiatives can be tailored to local contexts and scaled up to reach global audiences.
However, successful implementation hinges on a nuanced understanding of cultural nuances, socio-economic dynamics, and environmental priorities. Collaborative efforts between governments, businesses, and civil society are essential to ensure the effectiveness and relevance of such endeavors on a global scale.
Despite the potential of internet-enabled green public welfare models, vigilant oversight is necessary to prevent greenwashing and ensure the integrity of sustainability initiatives. Governments play a pivotal role in enacting and enforcing regulations that hold corporations accountable for their environmental claims and actions. Likewise, civil society organizations and grassroots movements serve as watchdogs, scrutinizing corporate practices and advocating for transparency and accountability. By fostering a culture of responsible stewardship and consumer empowerment, robust governance frameworks can safeguard against the exploitation of environmental concerns for profit-driven motives.
Conclusion
Ant Forest has shown that responsibility for preserving the ecological environment isn’t a distant ideal; it is an actionable goal accessible to every individual. By gamifying environmental conservation and integrating it into daily routines, Ant Forest has empowered millions to make meaningful contributions to sustainability.
From the beginnings of “planting trees on mobile phones” to restore ecosystems, to the ambitious vision of “everyone owning one square meter” to establish protected areas, and last year’s innovative “magic ocean” initiative, culminating in today’s groundbreaking “ancient tree protection model,” Ant Forest is committed to engaging everyone into environmental conservation.
It embodies the idea that environmental protection is not merely a concept but a collective action, encompassing everyone’s participation and commitment. The platform’s success lies in fostering a sense of accomplishment and personal connection, transforming virtual actions into real-world impacts. It has not only incentivized eco-friendly behaviors but has also seamlessly bridged the gap between environmental protection and economic development.
Ant Forest has redefined public welfare practices, ensuring transparency and accountability, and creating a symbiotic relationship between ecological stewardship and economic empowerment. Looking ahead, Ant Forest’s model holds immense potential for global application. By tailoring similar initiatives to local contexts, other countries can harness the power of technology to promote sustainable development. However, ensuring the integrity of these initiatives requires vigilant oversight from governments and active participation from civil society.
Ant Forest exemplifies how digital platforms can drive environmental and social change, turning everyday actions into a collective force for good. It stands as a testament to the power of individual contributions in shaping a sustainable future for humanity and the planet.
Reference
All pictures are screenshots of the author’s user pages.
Zhao, M., & Abeysekera, I. (2024). The behaviour of FinTech users in the Alipay Ant Forest platform towards environmental protection. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 10(1), 100201.
Tao, Li., Seven years of charity: Ant Forest has agreed to donate more than 3.4 billion yuan and plant 475 million trees. 21st Century Business Herald, Aug 30, 2023
Ant Forest – Magical Ocean, How to synthesize in Alipay’s Magical Ocean? Ant Forest Co-Cultivation Network, Nov 30, 2022, https://www.myslhz.com/sqhy/
BiaNews, 200 million people “claim” protected areas in Ant Forest, Bia News, May 22, 2020, https://www.sohu.com/a/396995529_115060
Rapp, J., Gamification for social good: A Chinese mobile payments leader is making it fun to donate to charity, VML, Apr 12, 2018, https://www.vml.com/insight/gamification-social-good
Yang, Z., Kong, X., Sun, J., Zhang, Y. Switching to Green Lifestyles: Behavior Change of Ant Forest Users. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(9):1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091819
SMU City Perspectives team, Growing A Global Forest, https://cityperspectives.smu.edu.sg/article/growing-global-forest-0
Pi L., 小果子是大生态也是大生意,蚂蚁森林扶贫产品“MA沙棘”上线, Public Welfare Times, http://www.gongyishibao.com/html/gongyizixun/17927.html
China’s Ant Financial shows how digital clout can fight climate change, United Nation Environment Programme, Nov 3, 2017, https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/chinas-ant-financial-shows-how-digital-clout-can-fight-climate-change

